How are AI chatbots shaping mental health care?
Mental health care faces unprecedented demand in the middle of workforce shortages and long wait times for therapy. AI-powered chatbots are emerging as a scalable solution, offering immediate, confidential, and stigma-free access to mental health support. These tools are being designed to provide psychoeducation, track emotional well-being, and deliver evidence-based cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) interventions, all while preserving anonymity and accessibility.
AI chatbots act as digital companions, offering active listening and guided exercises that empower users to manage stress, anxiety, or depression. They serve as the first line of support, bridging the gap between clinical visits and providing early intervention opportunities.
What are the main benefits of AI chatbots in mental health?
- 24/7 Accessibility: Support is always available, regardless of geography or scheduling constraints.
- Reduced Stigma: Patients often feel more comfortable sharing sensitive thoughts with non-human agents.
- Continuous Monitoring: Chatbots can track users’ emotions over time through conversational cues.
- Bridging Care Gaps: They reinforce therapy between sessions and ensure continuity of care.
- Personalization: AI algorithms tailor interactions based on users’ language, tone, and emotional patterns.
These benefits make chatbots valuable allies in preventive care and chronic condition management, particularly for mild to moderate mental health conditions.
How do AI chatbots work in mental health contexts?
AI chatbots leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand, interpret, and respond empathetically to user inputs. Key capabilities include:
- Sentiment Analysis: Detecting emotional states such as sadness, anger, or anxiety.
- Intent Recognition: Understanding what users seek, whether reassurance, information, or guidance.
- Crisis Detection: Identifying phrases that indicate suicidal ideation or acute distress.
- Adaptive Dialogue: Adjusting tone and complexity to match the user’s comfort level.
These systems can be integrated with electronic health record (EHR) systems or patient portals, providing clinicians with contextually enriched summaries for follow-up.
Ethical considerations and limitations
Safety, ethics, and trust are paramount when deploying AI chatbots in mental health care. Key concerns include:
- Transparency: Users must clearly understand they are interacting with an AI system, not a human clinician.
- Escalation Protocols: Chatbots should have predefined workflows to connect users to trained professionals during crises.
- Bias Control: Models must be trained on diverse, representative datasets to avoid demographic or linguistic biases.
- Privacy and Security: Encrypted data transmission and anonymization protocols are essential for compliance with HIPAA and GDPR.
- Informed Consent: Users must be aware of what data is collected and how it is used.
Ethical chatbots must balance accessibility with safety, providing emotional support without exceeding their predefined scope.
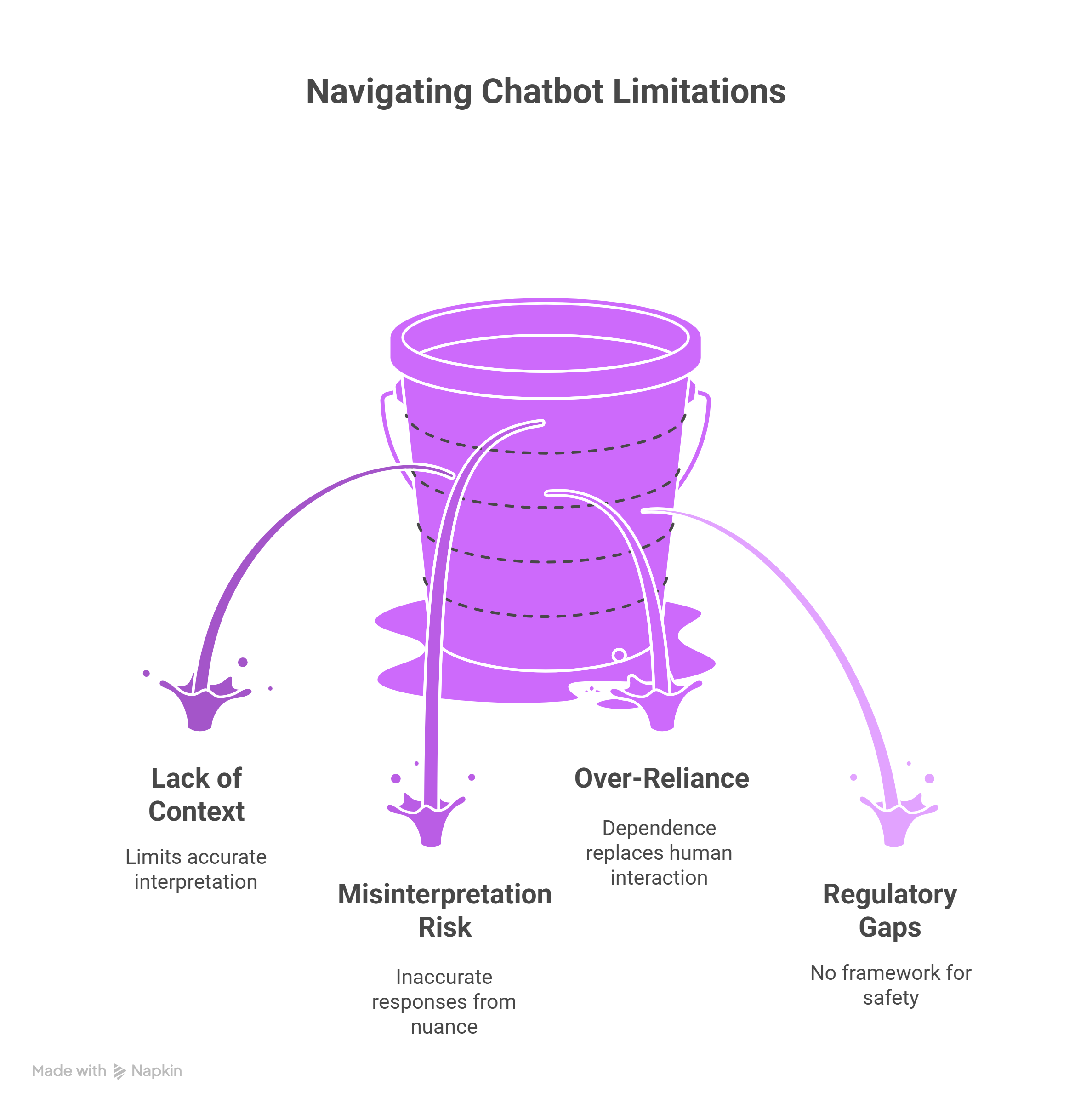
What are the limitations of AI chatbots for mental health?
While chatbots can extend care access, they are not replacements for professional therapy. Limitations include:
- Lack of deep contextual understanding: AI cannot fully interpret complex human experiences.
- Risk of misinterpretation: Emotional nuance or sarcasm can lead to inaccurate responses.
- Over-reliance: Users might depend on chatbots instead of seeking human help when necessary.
- Regulatory gaps: There is no universal framework for evaluating chatbot safety and clinical efficacy.
Ongoing research and hybrid human-AI care models can help mitigate these limitations.
Future directions: What’s next for mental health AI?
The next generation of AI chatbots will combine multimodal inputs (text, voice, facial cues) with adaptive emotional intelligence to create more human-like, responsive experiences. Key future trends include:
- Human-in-the-loop systems: Blending automation with clinical oversight for quality assurance.
- Personalized therapy plans: Using longitudinal data to adapt interventions dynamically.
- Regulatory-grade transparency: Providing interpretable AI frameworks for clinical validation.
These advancements will expand chatbots’ role from conversational support to more active care companions.
FAQs
Can chatbots replace therapists?
No. Chatbots complement professional care, providing scalable support and reinforcing therapy between sessions.
How can chatbot bias be mitigated?
By training models on diverse datasets, incorporating clinician review loops, and continuously monitoring for unintended bias.
Are AI chatbots clinically validated?
Some have been evaluated in controlled studies, showing positive results for anxiety and depression symptom management, though ongoing validation remains critical.
What ethical safeguards are essential?
Transparency, informed consent, data security, and emergency escalation mechanisms are fundamental.
Do users trust mental health chatbots?
Surveys show increasing trust when chatbots demonstrate empathy, privacy, and reliability.
Conclusion
AI chatbots represent a promising technology in digital mental health, that will hopefully help at expanding access to care through scalable, personalized, and confidential support. When built with transparency, ethical oversight, and emotional intelligence, they can significantly enhance patient engagement and continuity of care.