What is multimodal AI in healthcare?
Multimodal AI processes and combines information from multiple data types, such as clinical notes, medical images, and speech to provide a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s condition. Unlike unimodal models, which interpret a single source of information, multimodal AI mimics how clinicians integrate multiple signals, like lab results, imaging scans, and verbal reports to form a more complete picture of the patient. This integration enables more accurate diagnostics, context-aware decision support, and stronger predictive capabilities for personalized care.
Why is multimodal integration important?
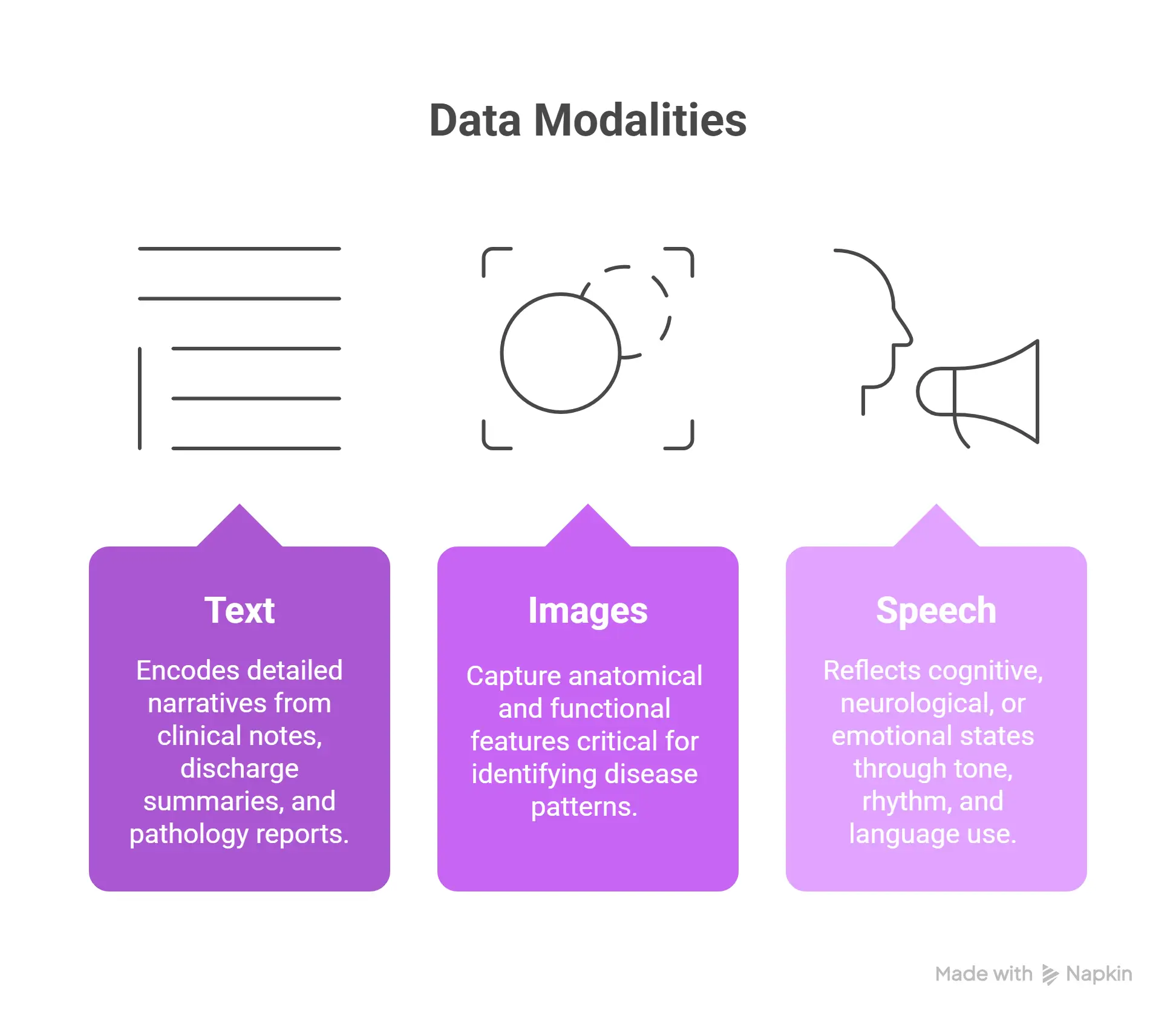
Each data modality reveals a different layer of clinical insight:
- Text: Encodes detailed narratives from clinical notes, discharge summaries, and pathology reports.
- Images: Capture anatomical and functional features critical for identifying disease patterns.
- Speech: Reflects cognitive, neurological, or emotional states through tone, rhythm, and language use.
By merging these data streams, multimodal AI enables contextual reasoning, a step closer to how human clinicians synthesize diverse information sources. This approach supports a more personalized care, especially in complex or multidisciplinary cases.
What are the core technologies behind multimodal AI?
- Transformer architectures that align features from text, vision, and audio data.
- Medical Vision-Language Models (VLMs) trained on aligned imaging-text pairs.
- Cross-modal embeddings enabling models to represent multiple data types within a unified space by the intelligent use of contrastive learning techniques that help models associate patterns across modalities.
These innovations allow AI systems to translate between modalities, for example, identifying the textual descriptors that best correspond to an image or summarizing imaging findings in natural language.
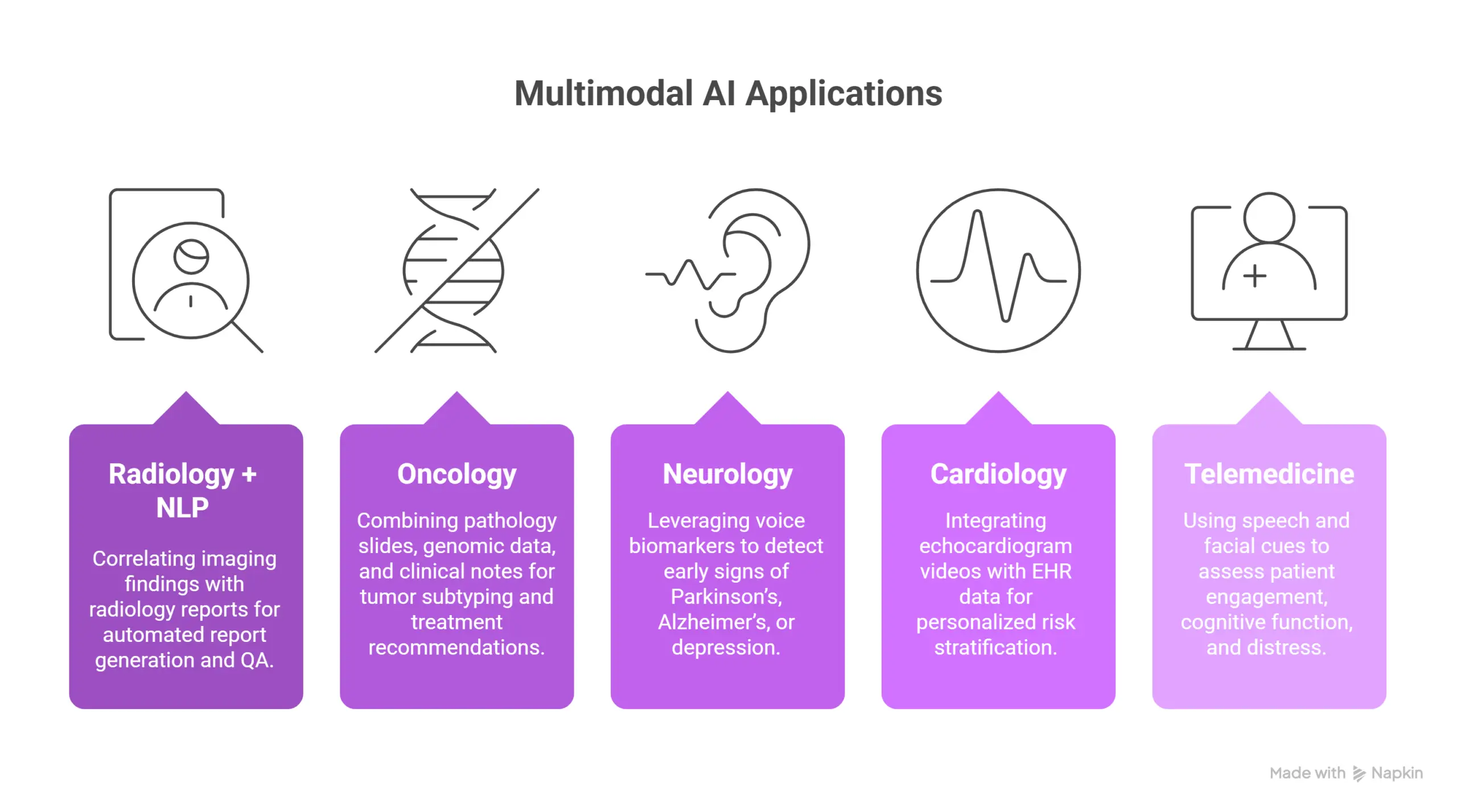
What are the key applications in clinical practice?
- Radiology + NLP: Correlating imaging findings with radiology reports for automated report generation and QA.
- Oncology: Combining pathology slides, genomic data, and clinical notes for tumor subtyping and treatment recommendations.
- Neurology: Leveraging voice biomarkers to detect early signs of Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, or depression.
- Cardiology: Integrating echocardiogram videos with EHR data for personalized risk stratification.
- Telemedicine: Using speech and facial cues to assess patient engagement, cognitive function, and distress.
How does multimodal AI enhance clinical decision-making?
Multimodal models support clinicians by:
- Reducing diagnostic ambiguity through cross-referencing text and image data.
- Automating reporting workflows, reducing administrative burden.
- Improving explainability via cross-modal attention maps that visually and linguistically help to understand better the predictions provided by the models.
What are the challenges and solutions?
- Data Integration and Synchronization
Different data types often exist in siloed systems with incompatible formats. Solutions include standardized ontologies (e.g., SNOMED CT) and multimodal data lakes built on interoperable standards (FIHR, OMOP-CDM).
- Labeling and Annotation Costs
Multimodal training requires precisely aligned annotations across modalities. Semi-supervised and active learning methods help reduce labeling effort.
- Privacy and Security
Patient confidentiality is paramount. Federated multimodal learning aims to enable cross-institutional model training without moving sensitive data.
- Explainability and Regulation
Multimodal models must offer transparent reasoning. Techniques like cross-attention visualization, gradient attribution or other post-hoc explainability methods help interpret how inputs from different modalities influence decisions.
How does John Snow Labs support multimodal AI development?
John Snow Labs’ Medical VLM-24B exemplifies multimodal intelligence combining visional and language reasoning for precise interpretation of clinical images.
These types of models allow healthcare institutions to deploy multimodal AI safely and effectively, enhancing diagnostics and clinical workflows while fulfilling HIPAA and GDPR requirements.
The future of multimodal AI in healthcare
The next evolution of multimodal AI will focus on contextual intelligence, systems that understand not just medical data, but clinical intent. Key trends include:
- Multimodal foundation models trained on billions of healthcare data points.
- Real-time multimodal assistants supporting clinicians during diagnosis and surgery.
- Integration with wearable and sensor data, enriching patient monitoring and predictive care.
- Interoperable multimodal ecosystems connecting hospital systems, research labs, and telehealth networks.
As these technologies mature, multimodal AI will enable precision medicine at scale, bridging the gap between fragmented data and unified, actionable intelligence.
FAQs
What makes multimodal AI different from standard AI?
It integrates multiple data types, text, images, and speech to deliver richer, context-aware insights.
What infrastructure is required?
High-performance GPUs, multimodal data storage solutions, and compliant data-sharing frameworks are essential.
Is multimodal AI explainable?
Yes to some extent. Modern multimodal systems use visual and linguistic attention mapping to improve explainability about how data input influences outcomes.
Conclusion
Multimodal AI marks a major step toward precision healthcare by unifying visual, textual, and audio information. With continued advances in model architecture, privacy-preserving learning, and cross-modal explainability, multimodal AI is well positioned to redefine how clinicians diagnose, communicate, and care for patients.
John Snow Labs remains at the forefront of this evolution, offering multimodal AI models that aim to support safer, smarter, and more connected healthcare.