The healthcare industry is approaching a defining moment. Artificial intelligence (AI), once a futuristic promise, is now becoming foundational to hospital operations. As AI capabilities evolve and regulatory frameworks mature, hospitals must begin planning for large-scale deployments in 2026. This article explores the strategic, technological, financial, and operational considerations necessary for healthcare leaders to realize the transformative potential of AI.
Understanding the Market Opportunity
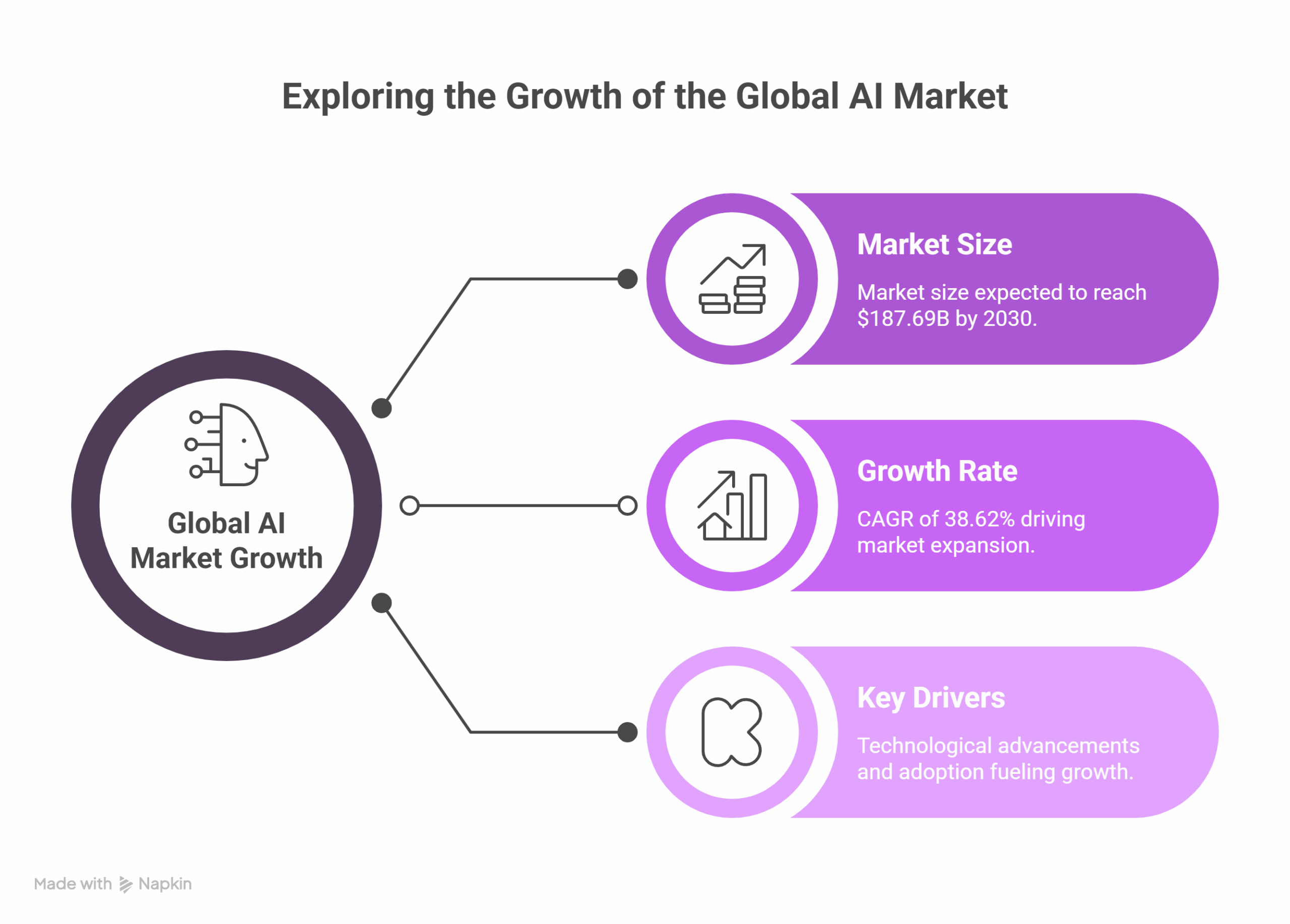
The global healthcare AI market is on a steep growth trajectory. Valued at $26.57 billion in 2024, it is projected to reach $187.69 billion by 2030, driven by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.62%[1]. North America leads the global market, while the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth[2]. In the U.S. alone, venture capital investments in healthcare AI reached $7.2 billion in 2023[3].
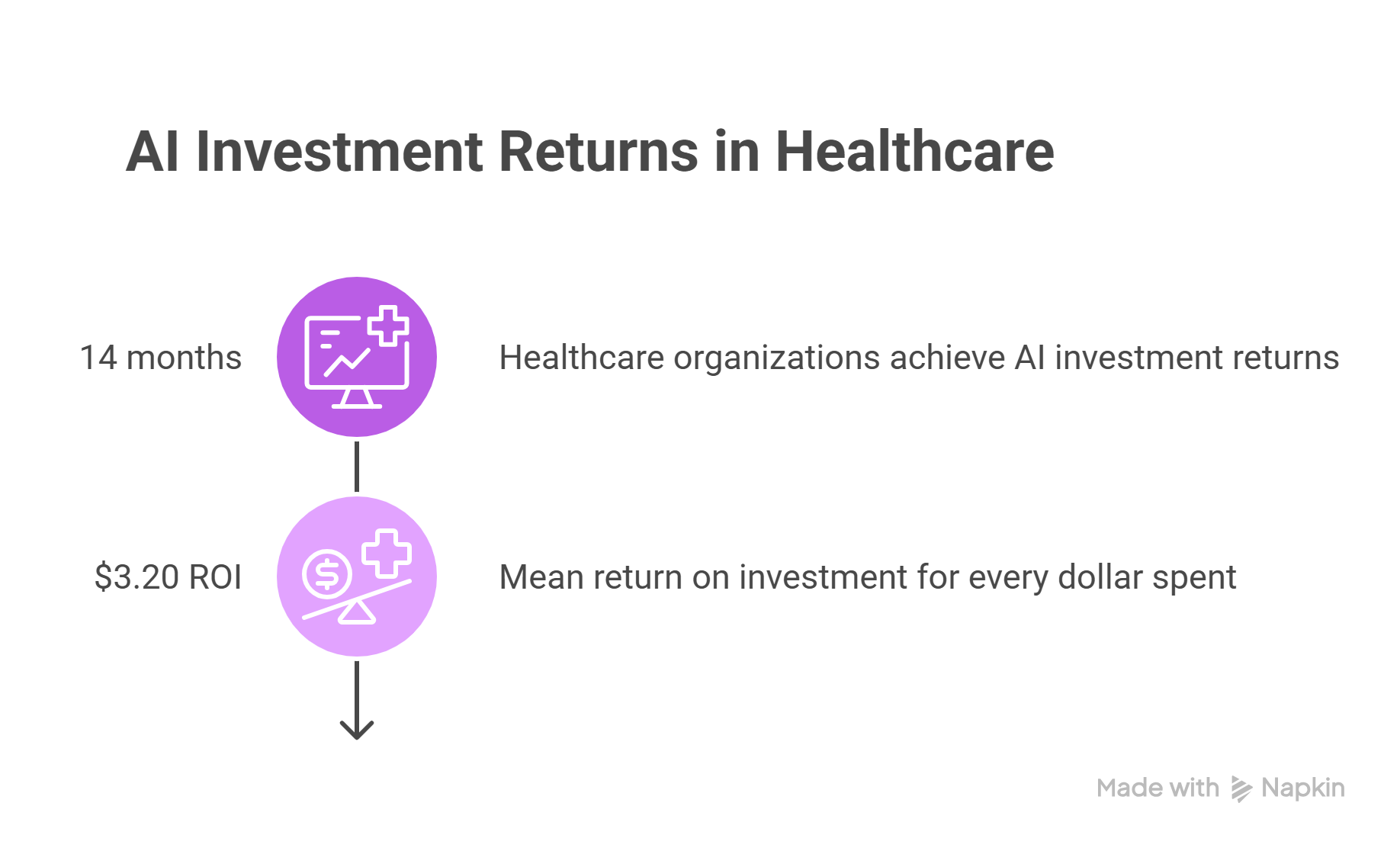
Hospitals exploring AI adoption can expect substantial returns. A 2023 Microsoft-commissioned IDC study found that healthcare organizations achieved a demonstrable return on AI investments within 14 months, with an estimated $3.20 mean ROI for every dollar spent on an AI project and initiative [4]. These gains stem from improved efficiency, reduced administrative burdens, and enhanced patient care.
Clinical Documentation AI: A Fast-Growing Priority
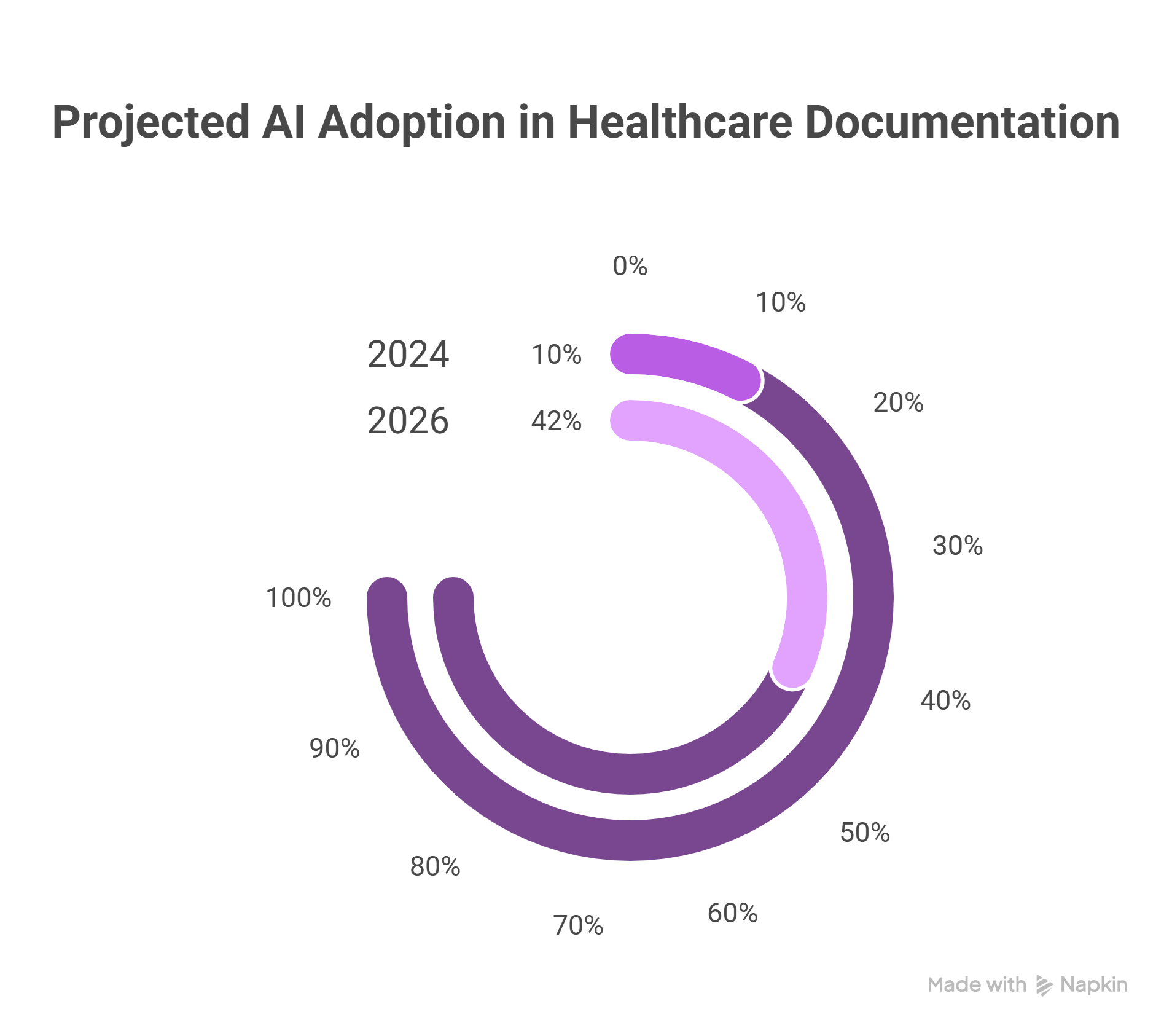
Clinical documentation is one of the most promising areas for AI implementation. Only 10% of healthcare executives currently use AI for documentation, but that number is expected to rise to 42% by 2026, a 320% increase[5]. At institutions like Stanford Health Care, 96% of physicians report satisfaction with AI-powered documentation tools, which save an average of two hours per day.
Early Movers: Hospitals Leading the Way
Mayo Clinic tops the CB Insights Hospital AI Readiness Index, having filed over 50 AI-related patents and invested in several startups[6]. Intermountain Health is using AI for clinical decision support[7], while Cleveland Clinic has partnered with PathAI to enhance diagnostic accuracy and research capabilities. These examples illustrate the competitive advantage of early AI adoption.
The Role of Healthcare NLP
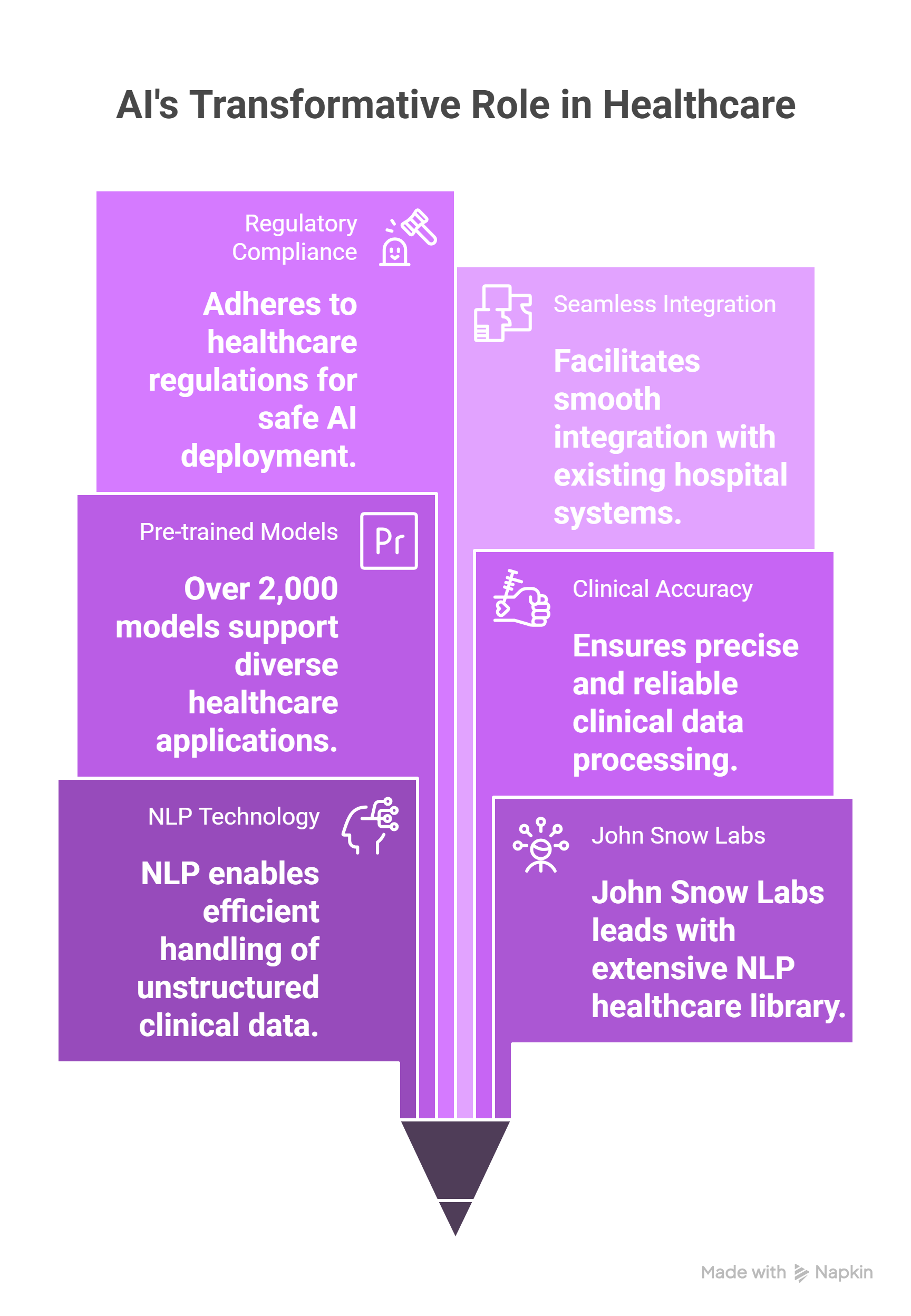
At the center of AI’s impact in hospitals is natural language processing (NLP), particularly for handling unstructured clinical data. John Snow Labs leads this field with the most widely used NLP library in healthcare, powering over 2,000 pre-trained models in more than 250 languages[8]. Its solutions are designed for clinical accuracy, regulatory compliance, and seamless integration[9].
Streamlining Documentation and Data Extraction
Up to 80% of medical data is unstructured, making it difficult to extract insights manually[10]. Healthcare NLP enables hospitals to automatically capture information from handwritten notes, voice recordings, and narrative clinical documentation. With transcription accuracies as high as 99%, speech to text technologies enhance EHR usability while reducing clinician workload.
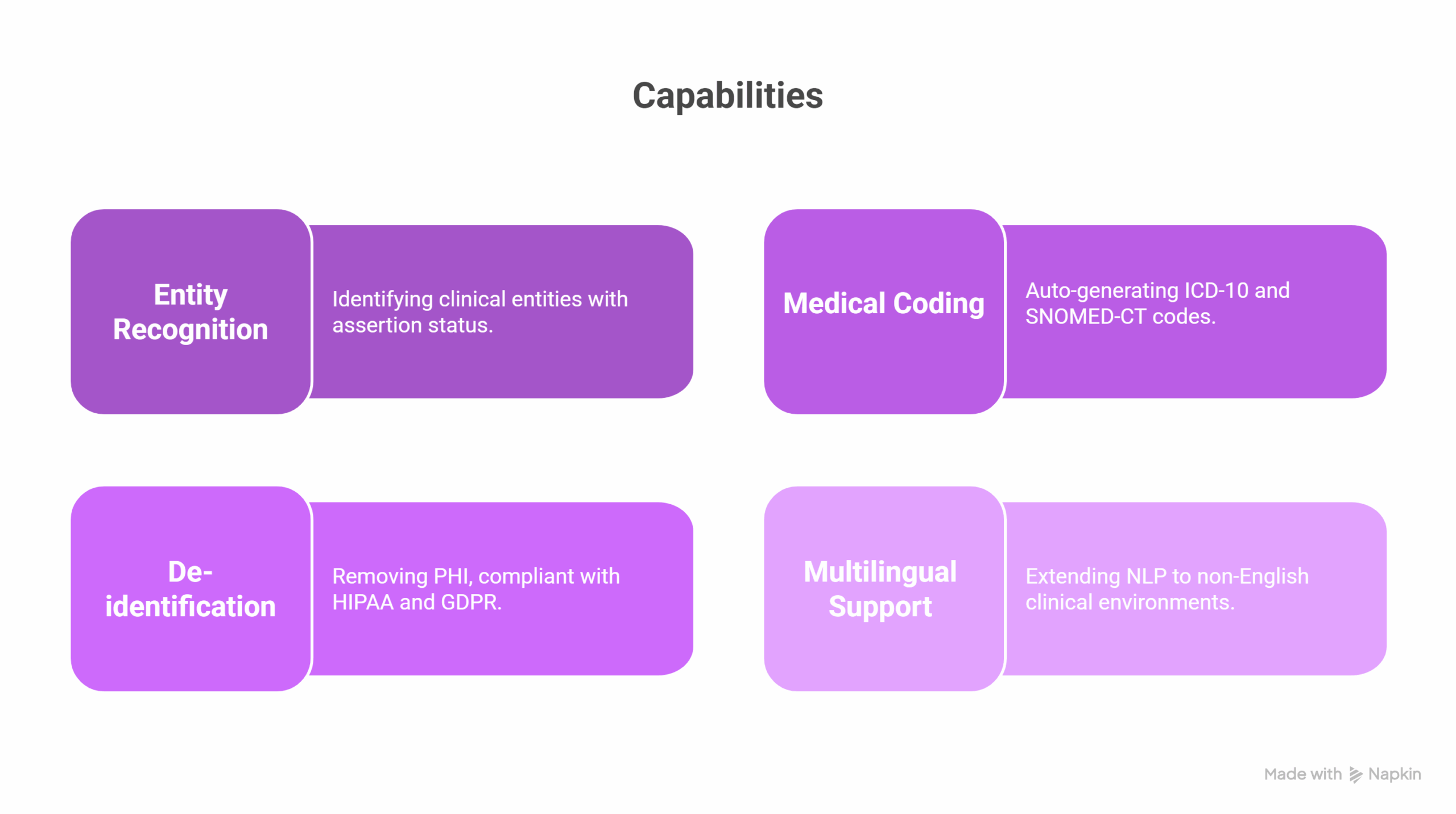
Clinical and Operational Applications
- Entity recognition: Identifying over 400 clinical entities, including assertion status (e.g., presence, negation, uncertainty)[11]
- Medical coding: Auto-generating ICD-10 and SNOMED-CT codes
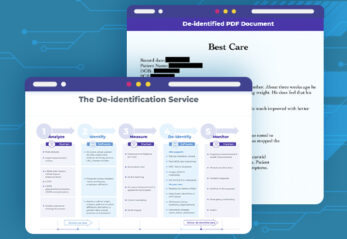
- De-identification: Compliant with HIPAA and GDPR for PHI removal [12]
- Multilingual support: Extending NLP to non-English clinical environments
Solving Data and EHR Challenges
Healthcare data silos, inconsistent formats, and legacy systems present real obstacles. Interoperability standards such as HL7 and FHIR help bridge gaps, while master data management ensures consistent patient records across systems [13]. API-driven architectures allow real-time streaming and integration with AI modules.
Budgeting for AI Implementation
The cost of AI deployment varies widely:
- Basic tools: $50,000–$500,000
- Custom platforms: $1-10 million
- Infrastructure: $100,000-$1 million annually
Hospitals can offset these investments through direct savings (e.g., reduced labor), improved quality outcomes, and increased patient throughput. Federal funding, private partnerships, and phased deployment strategies help spread costs over multiple years.
Typical Budget Allocation
- Development: 40-50%
- Deployment: 20-30%
- Maintenance: 30-50% annually
- Compliance and security: 15-25%
Navigating Compliance and Privacy
Compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and emerging AI regulations is essential.
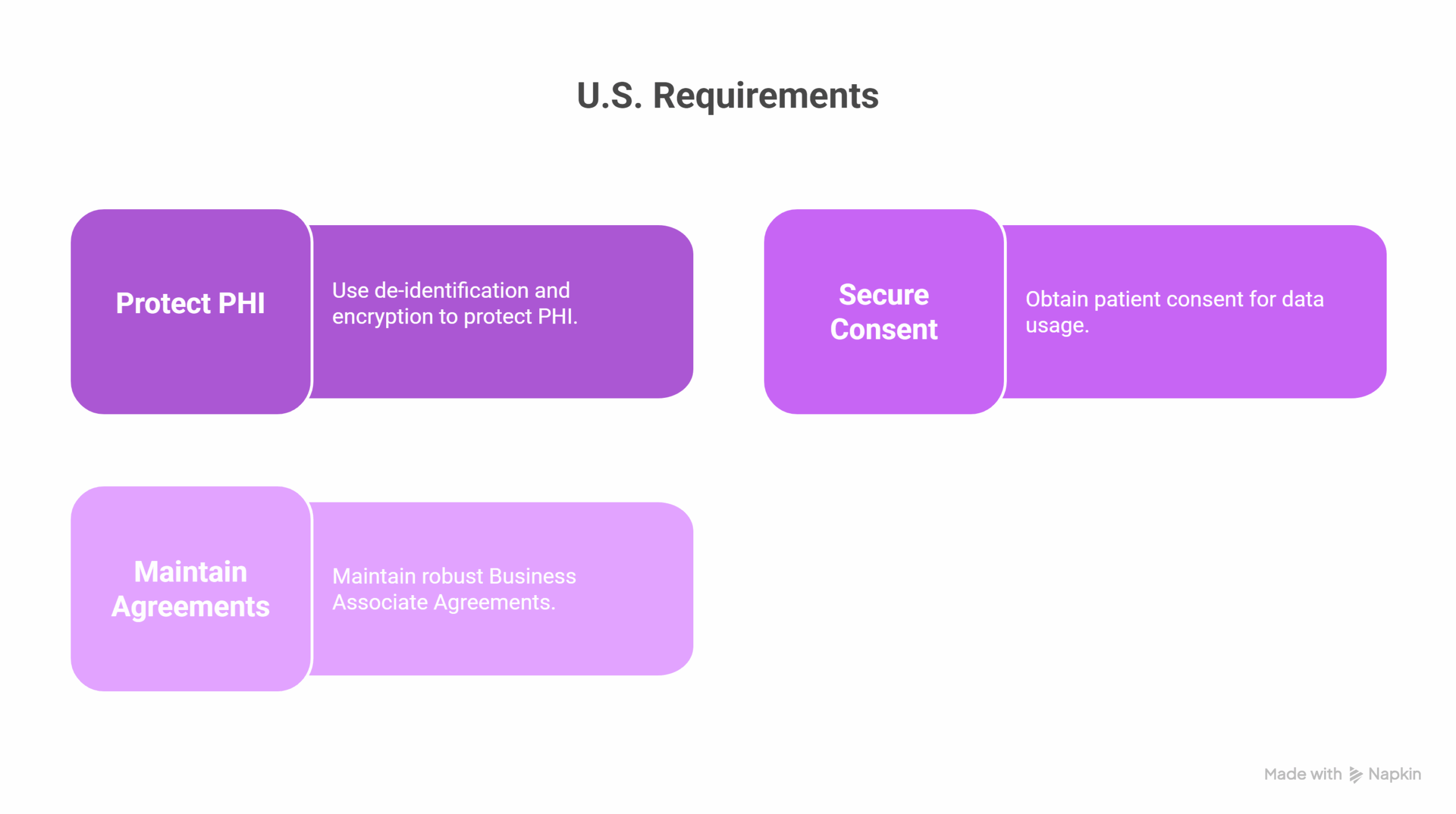
U.S. Requirements
- Protect PHI using de-identification and encryption
- Secure patient consent for data use
- Maintain robust Business Associate Agreements
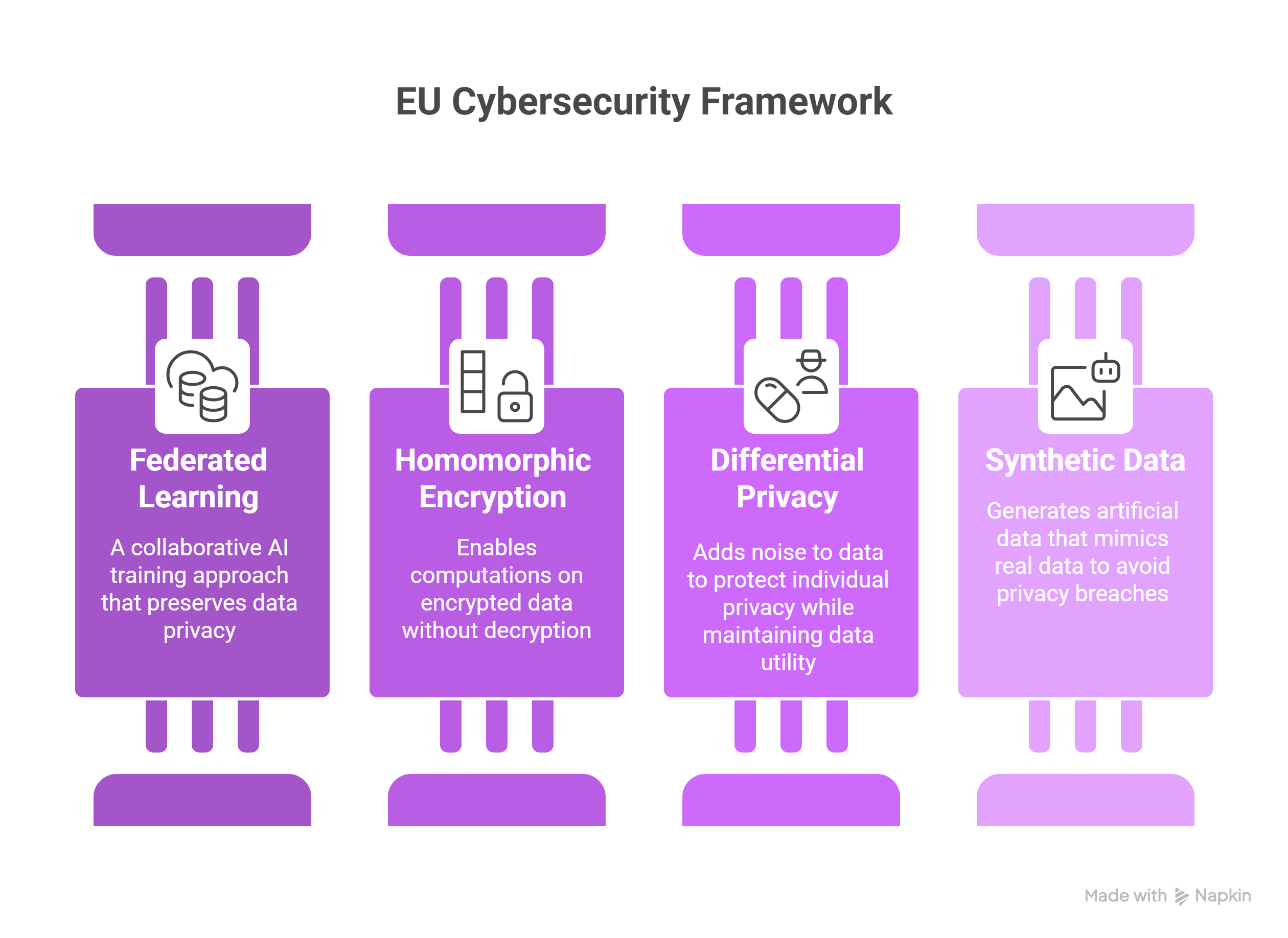
European Initiatives
- EU Cybersecurity Action Plan and the European Cybersecurity Support Centre[14].
- Privacy techniques: federated learning, homomorphic encryption, differential privacy, and synthetic data[15].
Regulatory Pathways
- FDA Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) framework [16]
- CE marking for EU compliance
- Post-market surveillance and quality management systems (e.g., ISO 13485)
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Workforce and Cultural Change
Hospitals face a shortage of AI-literate staff[17]. Solutions include:
- Structured training programs
- Phased implementation to reduce fatigue
- Sharing success metrics to drive cultural adoption
Integration and Security
- Use of FHIR/HL7 for interoperability
- Secure APIs and validated data migration
- AI-driven cybersecurity and Zero Trust frameworks[18]
Best Practices for AI Success
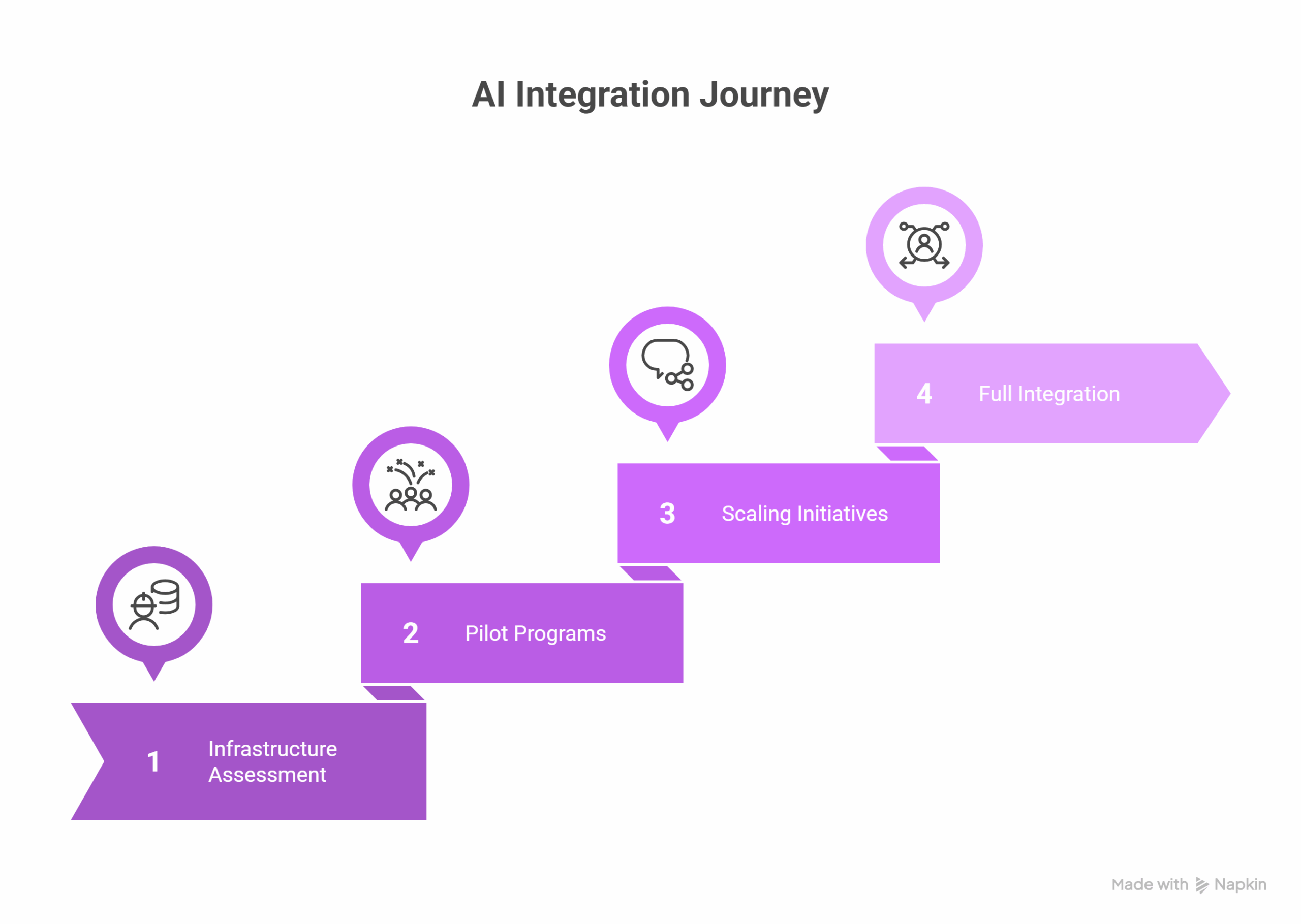
Hospitals should assess AI readiness across eight pillars: strategy, data, technology, people, culture, processes, governance, and ethics[19]. A phased approach, starting with foundational investments, followed by pilots and scaling, provides a manageable path to full deployment.
Leadership matters. Appointing a Chief AI Officer, establishing a Center of Excellence, and forming an AI Ethics Board can significantly improve outcomes. Partnerships with academia, vendors, and government programs amplify capabilities.
Looking Ahead: AI’s Transformative Potential
Predictive Analytics and Precision Medicine
AI enables risk stratification, personalized treatments, and real-time clinical guidance. These tools also support large-scale population health monitoring.
Virtual and Remote Care
AI is integral to telemedicine, remote monitoring, and triage. Chatbots and IoT-powered platforms improve patient engagement and care coordination.
Population Health and Health Equity
AI models can incorporate social determinants of health to predict outcomes and design preventive interventions, advancing both health equity and epidemiological surveillance.
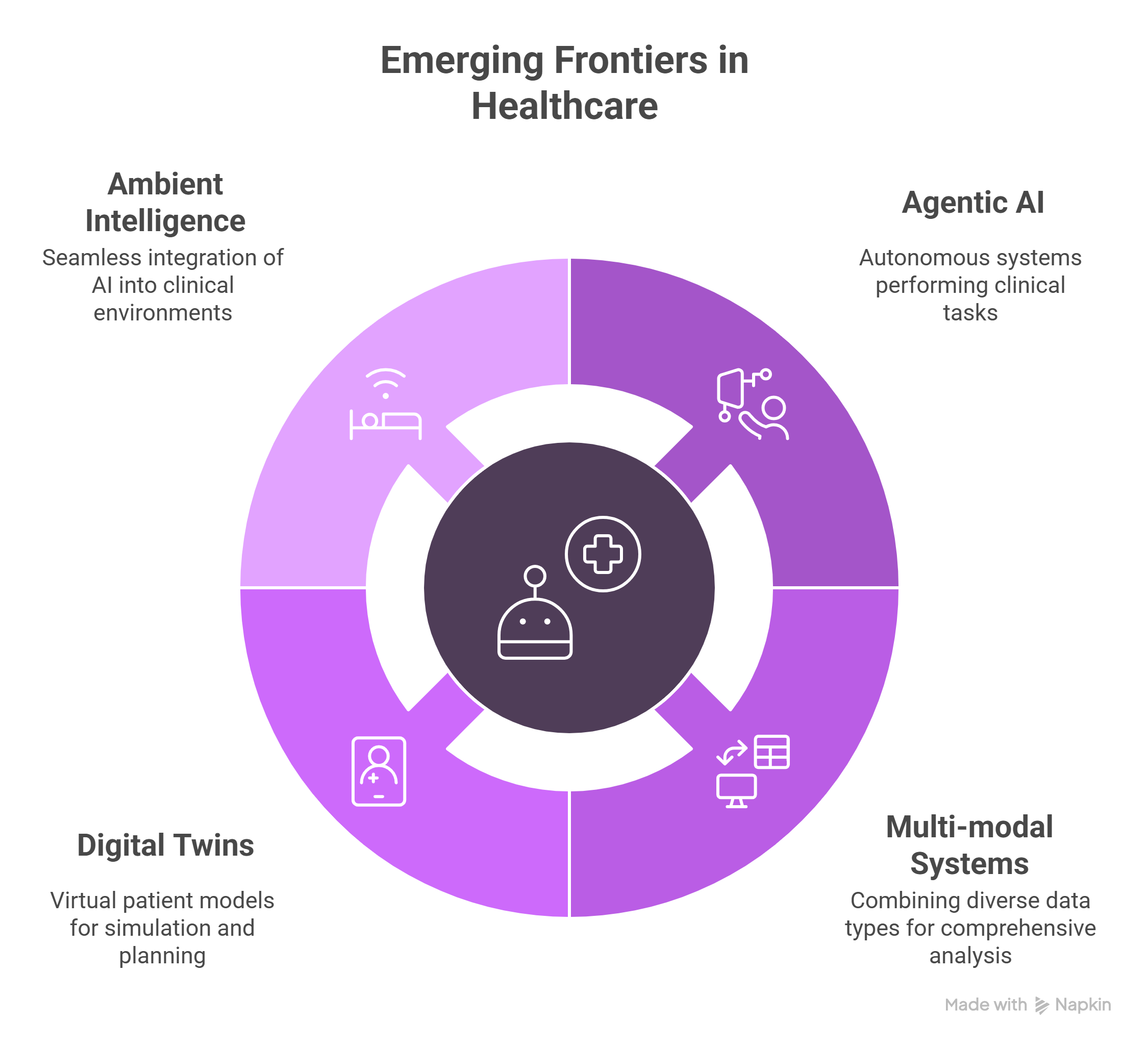
Emerging Frontiers
- Agentic AI: Autonomous systems for clinical tasks
- Multi-modal systems: Combining image, text, and sensor data
- Digital twins: Virtual patient models for simulation and planning
- Ambient intelligence: Seamless integration into clinical environments
Global Perspectives
North America remains the global leader in healthcare AI innovation and regulation. Asia-Pacific’s rapid growth is fueled by government initiatives and demographic trends. Europe’s emphasis on ethics and privacy positions it as a regulatory thought leader[20]. Global collaboration is accelerating through WHO standards, cross-border research, and harmonized approvals.
Hospitals should measure outcomes across clinical quality, efficiency, financial ROI, and satisfaction. Risk management plans must address technology, compliance, cost, and workforce disruptions.
Final Thoughts: Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
AI in healthcare is not just a technology investment, it is a systemic transformation. Hospitals that succeed will be those that pair cutting-edge tools with responsible implementation, strong governance, and a relentless focus on patient outcomes.
Healthcare NLP, predictive analytics, and AI-powered clinical decision support are changing how care is delivered. The future demands bold vision, rigorous planning, and a steadfast commitment to safety, equity, and impact.
FAQs
What is the ROI for hospital AI investments?
Some hospitals report a return of $3.20 per dollar invested, often within 14 months.
How can hospitals train staff for AI integration?
Through structured training, continuous education, and embedding AI into clinical workflows.
What regulations must medical AI comply with?
In the U.S., HIPAA and FDA SaMD rules apply. In the EU, GDPR and CE marking are key.
What’s the biggest infrastructure hurdle?
Legacy EHRs and fragmented data. APIs, cloud platforms, and FHIR can help.
Can AI improve patient outcomes?
Yes. From faster diagnosis to predictive care, AI supports better clinical decisions.
Supplementary Q&A
How does federated learning protect patient privacy?
By training models locally and sharing only the updates, federated learning reduces data exposure.
What’s the role of synthetic data in healthcare AI?
It allows model training without exposing real patient data, supporting compliance and innovation.
References
[1] Grand View Research – AI In Healthcare Market Size, Share | Industry Report, 2030[2] GM Insights – AI in Healthcare Market Trends Report, 2032 | Industry Insights
[3] Silicon Valley Bank – AI in Healthcare Report
[4] Intel – Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare and Life Sciences
[5] Healthcare Dive – This healthcare AI use case will grow 320% by 2026, survey finds
[6] Becker’s Hospital Review – Top 25 hospitals for AI readiness
[7] Healthcare IT News – Intermountain launches interoperable, real-time CDS platform
[8] John Snow Labs – Healthcare AI Company
[9] John Snow Labs – Natural Language Processing in Healthcare | Medical NLP Tools
[10] ForeSee Medical – Natural Language Processing in Healthcare
[11] Microsoft Azure Marketplace – John Snow Labs – Healthcare NLP
[12] AWS Marketplace – John Snow Labs – Healthcare NLP
[13] PMC – A comprehensive overview of barriers and strategies for AI
[14] Sidley – EU Commission Launches Cybersecurity Action Plan for Hospitals
[15] PMC – Data Privacy in Healthcare: In the Era of Artificial Intelligence
[16] Paragon Institute – Healthcare AI Regulation: Guidelines for Maintaining Public Safety
[17] PMC – A comprehensive overview of barriers and strategies for AI
[18] Paubox – AI in healthcare privacy: Enhancing security or introducing new risks?
[19] Agility at Scale – AI Readiness Blueprint: Preparing Your Organization for AI Adoption
[20] IDC Blog – AI-Powered Healthcare in Asia Pacific: What’s Next for 2025 and Beyond