This post presents a comparative benchmark of medical Vision Language Models (VLMs) evaluated on a range of clinically relevant visual and multimodal tasks. The study focuses on assessing how well specialized medical models perform in comparison with large general-purpose foundation models when interpreting medical images together with clinical context.
We compare JSL-VL-7B and JSL-VL-8B, two domain-specific models developed by John Snow Labs for healthcare applications, against several leading foundation models, including Intern-VL-30B, and Qwen3-VL-32B.
The main objective of this evaluation is to understand how these models perform in real-world clinical scenarios, particularly for tasks such as medical information extraction, image-based question answering, and medical reasoning.
Models evaluated
We chose these models to include both specialized medical models and large general-purpose models. This allows us to compare their performance on both medical-specific tasks and broader vision-language tasks:
- InternVL3_5–30B-A3B: A multimodal foundation model trained on diverse datasets.
- Qwen3-VL-32B-Instruct: A large-scale general-purpose vision-language model.
- JSL-VL-7B: A medical VLM optimized for clinical document and image understanding.
- JSL-VL-8B: A variant with improved multimodal reasoning capabilities.
Evaluation datasets and results
We evaluated the models using four complementary datasets that cover both visual and textual medical tasks. In this section, we describe each dataset and present the corresponding results to show how the models perform across different types of data.
Evaluation Methodology: All models were evaluated in zero-shot settings using standardized prompts. Performance metrics include precision, recall, F1-score, accuracy and Hallucination Rate, depending on the task.
MedJSLPrint
This dataset is based on 30 printed clinical documents, expanded to 256 images through data augmentation for evaluation.
The documents contain printed medical text and were processed to simulate realistic conditions such as noise, blur, scanning artifacts, uneven lighting, and degraded quality.
It is divided into two subsets:
- 196 images for medication extraction.
- 60 images for medication and medical test extraction.
Here’s a sample from the dataset:

Image and Annotation from MedJSPrint dataset
Now, let’s take a look at the results:
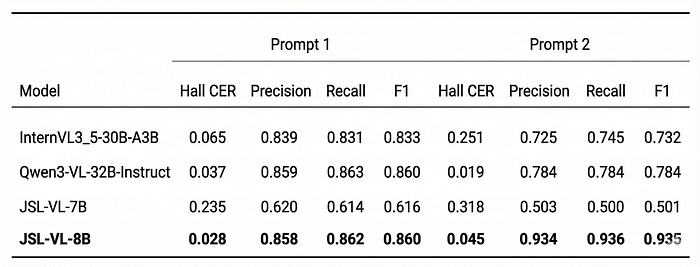
Evaluation on MedJSLPrint dataset. *Prompt1: Extract medicine names, *Prompt2: Extract medicine names and medical tests
MedJSLHw
This dataset contains 96 handwritten medical prescriptions from Kaggle, annotated by John Snow Labs.
The prescriptions include realistic, often hard-to-read handwriting. The dataset is for evaluating models that extract medications from handwritten notes.
Here’s a sample from the dataset:

Image and Annotation from MedJSLHW dataset
Let’s see the results now:
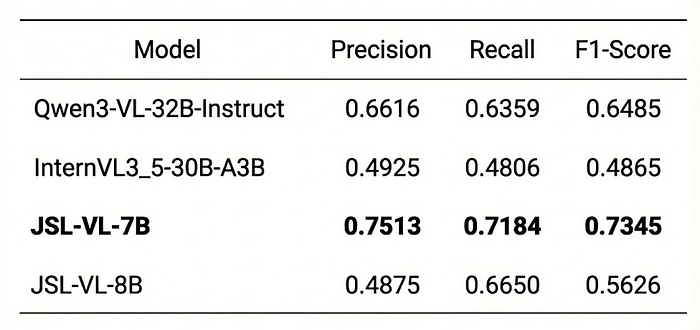
Evaluation on MedJSLHw
OmniMedVQA-MRI
This dataset is a subset of the OmniMedVQA dataset. It contains 31,917 MRI images and is used for medical image understanding and visual question answering tasks on MRI scans.
Here’s a sample from this dataset:
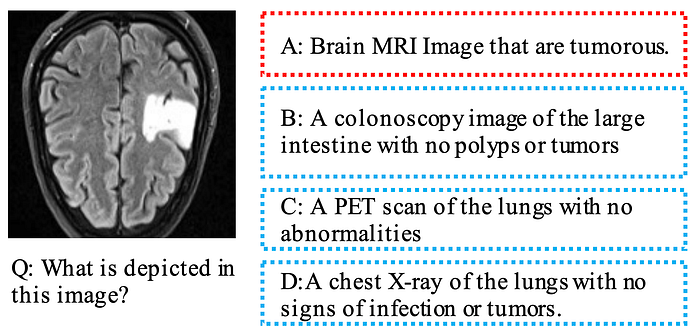
Image and Annotation from OmniMedVQA-MRI
Here are the results:
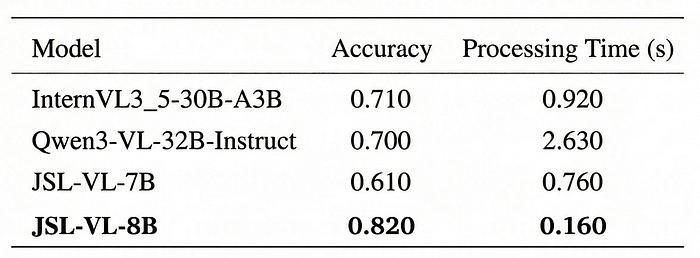
Evaluation on OmniMedVQA-MRI
MedXpertQA
MedXpertQA is a challenging benchmark for expert-level medical knowledge and reasoning, with 4,460 questions covering 17 specialties and 11 body systems. It has two subsets: Text, for text-only evaluation, and MM, for multimodal evaluation with images, patient records, and exam results.
We use Inspect AI to evaluate this dataset, focusing on the textual capabilities of language models in medical reasoning, question answering, and domain knowledge.
Here’s a sample from this dataset:

Sample from MedXpertQA
Now, let’s take a look at the results:
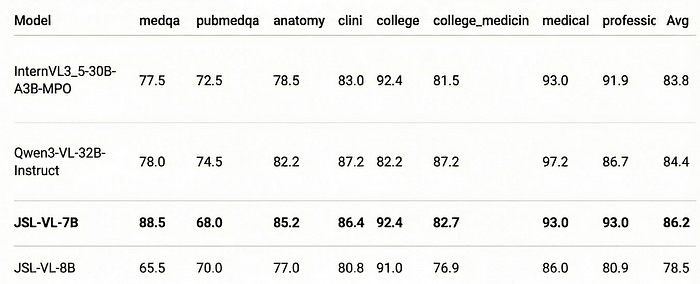
Evaluation on MedXpertQA
Key takeaways
Here’s what we learned from our benchmark:
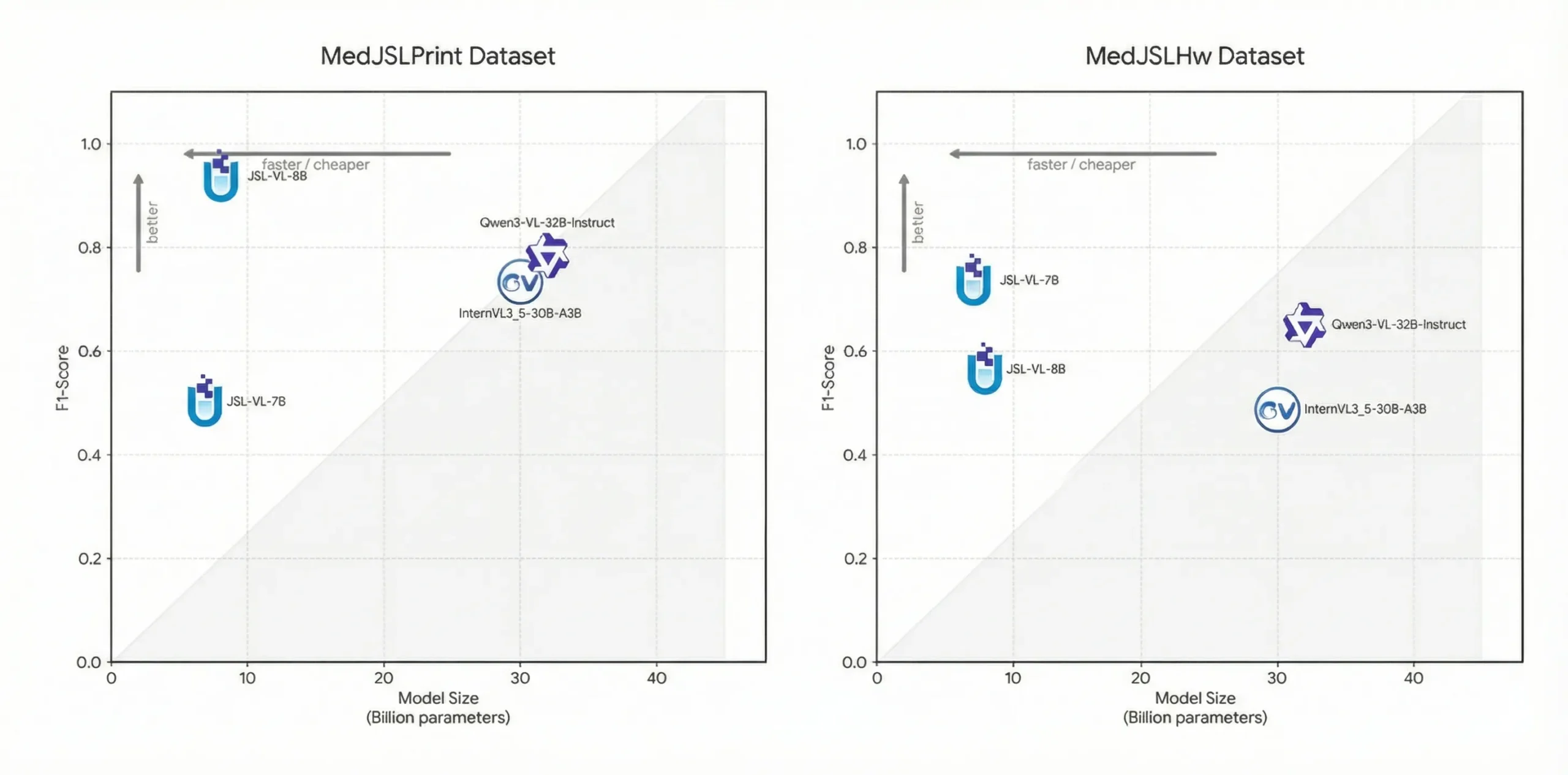
Models Benchmark Summary
Medical models shine in clinical tasks
- JSL-VL-7B performs best at extracting medications from handwritten prescriptions, while JSL-VL-8B excels with printed prescriptions and medical tests.
Handwritten notes are still tricky
- Handwritten prescriptions remain challenging, but JSL-VL-7B handles them very well compared to other models.
Domain knowledge matters
- In text-based reasoning tasks, medical-trained models give more accurate and clinically meaningful answers.
The Big Picture:
For real-world healthcare applications, specialized medical VLMs outperform general-purpose models. They are more precise, reliable, and better at handling medical terminology, essential for tasks like prescriptions, lab tests, and diagnostic interpretation.
Deployment and access
These models are part of the Visual NLP (VNLP) library, which has its own license and includes a growing set of medical AI features and models.
They can be deployed using Databricks container services and model serving endpoints, making them suitable for scalable production environments. Detailed deployment guides are available in the following blogposts:
- Deploying John Snow Labs Medical LLMs on Databricks: Three Flexible Deployment Options
- Scaling John Snow Labs Medical LLMs on Databricks environments
A practical example is available in the following notebook:
Resources
- John Snow Labs Models
- JSL datasets
- Kaggle dataset
- OmniMedVQA
- MedXpertQA
- Inspect AI
- Usage of Model Serving endpoints Notebook
- Scaling John Snow Labs Medical LLMs on Databricks environments
- Deploying John Snow Labs Medical LLMs on Databricks