How are conversational agents transforming patient education?
Conversational agents, commonly known as chatbots or virtual assistants, are becoming vital tools in healthcare. They provide patients with accessible, interactive, and personalized information outside traditional clinical visits. For patient education programs, these AI-driven tools are particularly powerful, offering continuous engagement, real-time support, and scalable education across diverse populations.
As patients increasingly seek digital health resources, conversational agents bridge the gap between clinical expertise and patient self-management. They deliver medical information in simple, conversational language, empowering patients to understand conditions, treatments, and preventive care better.
Why is patient education critical in modern healthcare?
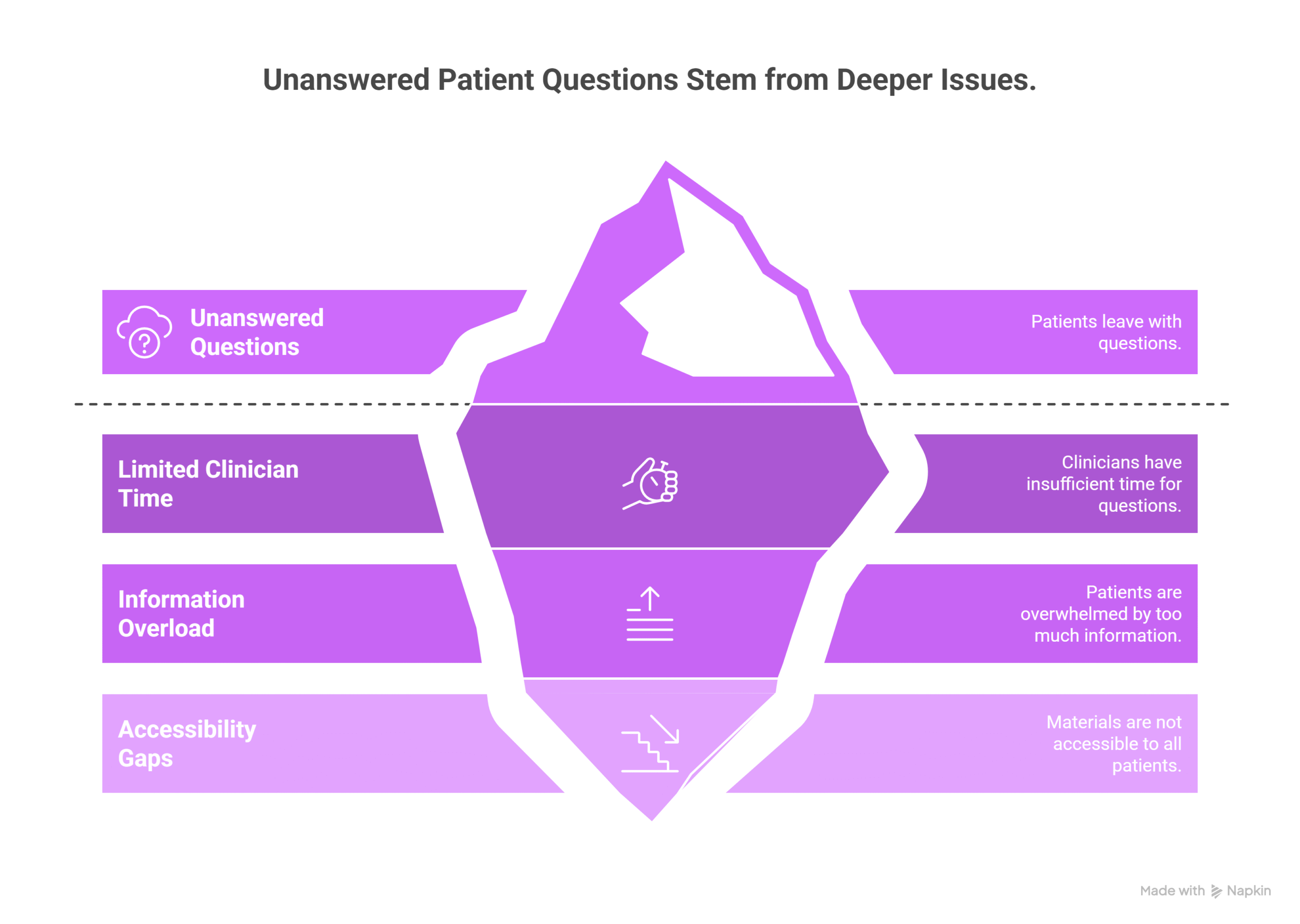
Effective patient education improves health literacy, treatment adherence, and outcomes. Yet, challenges remain:
- Limited clinician time: Patients often leave appointments with unanswered questions.
- Information overload: Handouts and online articles can overwhelm patients.
- Accessibility gaps: Non-native speakers and patients with lower literacy may struggle with traditional materials.
What are the key benefits of conversational agents in patient education?
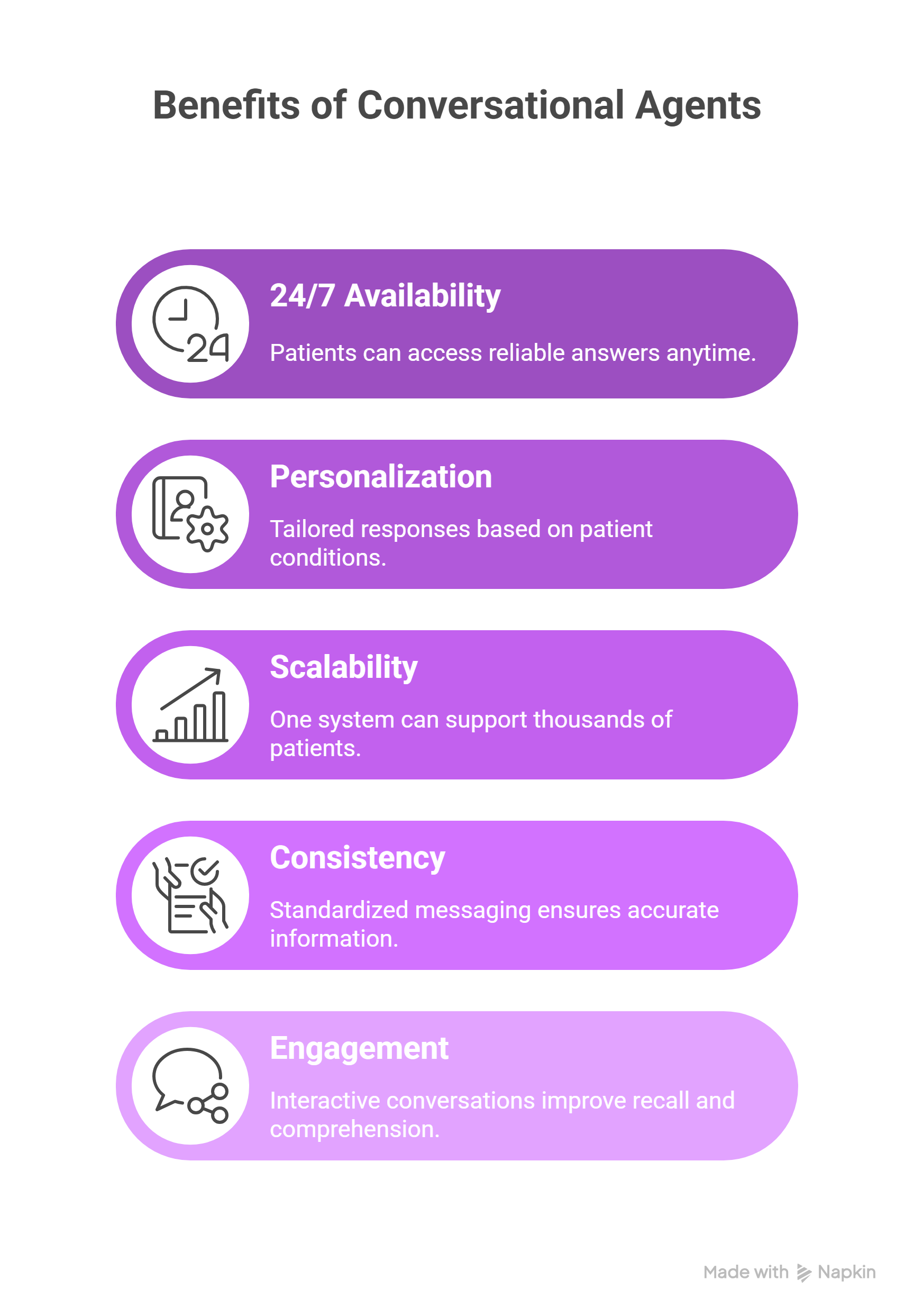
- 24/7 Availability: Patients can access reliable answers anytime without waiting for clinic hours.
- Personalization: Tailored responses based on patient conditions, demographics, and treatment history.
- Scalability: One system can support thousands of patients simultaneously, easing provider workloads.
- Consistency: Standardized messaging ensures patients receive accurate and evidence-based information.
- Engagement: Interactive conversations improve recall and comprehension compared to static materials.
 How do conversational agents support patient education programs?
How do conversational agents support patient education programs?
Conversational agents can be integrated into patient journeys at multiple touchpoints:
- Pre-visit preparation: Explaining procedures, necessary documents, or fasting instructions.
- Post-visit follow-up: Reinforcing medication schedules, side effect monitoring, or rehabilitation exercises.
- Chronic disease management: Educating patients on lifestyle modifications and symptom tracking.
- Preventive care: Promoting vaccinations, screenings, and wellness activities.
For example, a patient with diabetes can interact with a chatbot that explains insulin usage, tracks blood sugar trends, and provides reminders for eye and foot exams.
What technologies power conversational agents in healthcare?
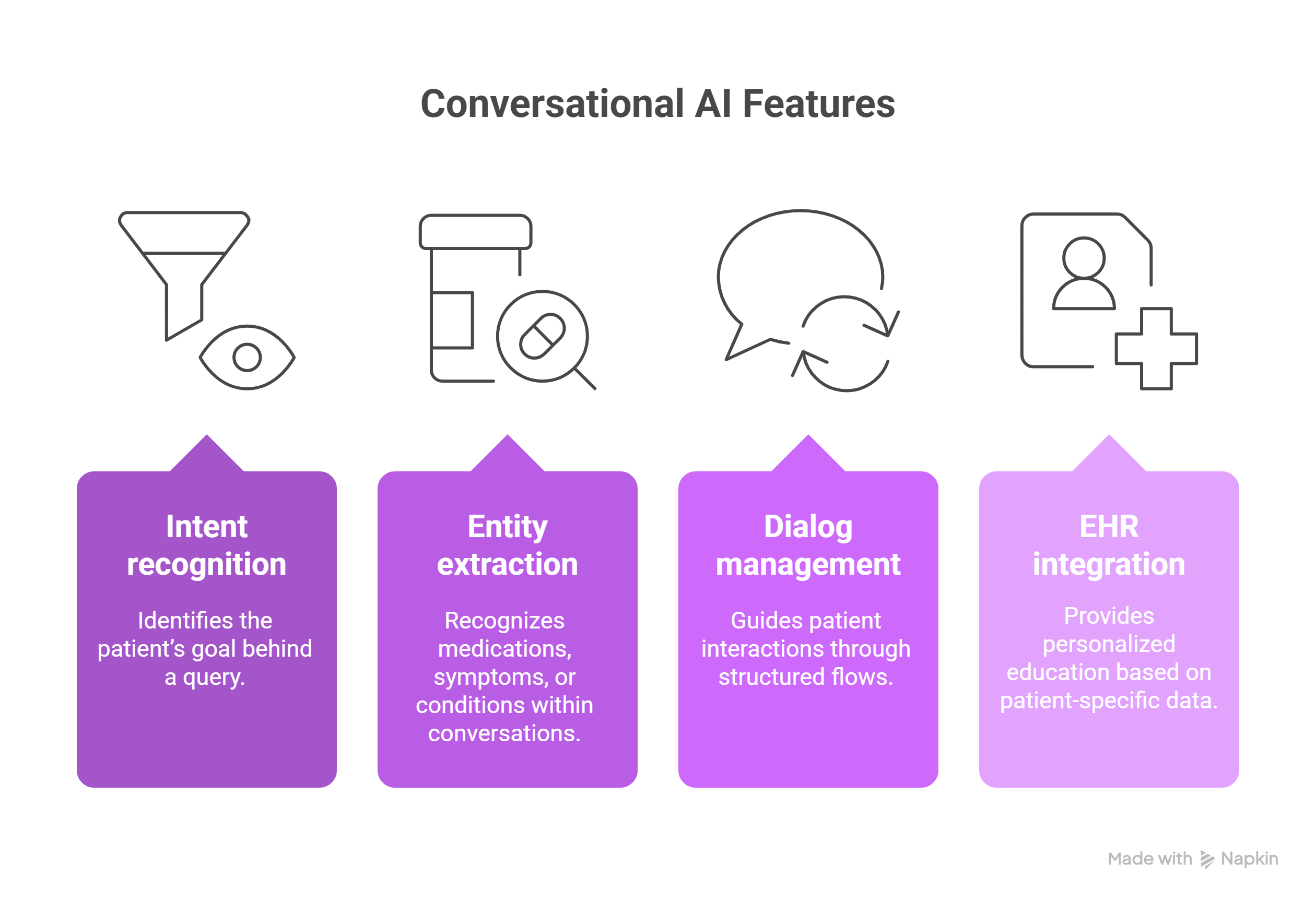
Healthcare conversational agents rely on advanced NLP (Natural Language Processing) and LLMs (Large Language Models) to interpret patient queries and respond with clinically validated content. Key technologies include:
- Intent recognition: Identifies the patient’s goal behind a query.
- Entity extraction: Recognizes medications, symptoms, or conditions within conversations.
- Dialog management: Guides patient interactions through structured flows.
- Integration with EHRs: Provides personalized education based on patient-specific data.
What challenges must be addressed for safe adoption?
While conversational agents offer significant potential, challenges include:
- Accuracy and reliability: Ensuring content is evidence-based and regularly updated.
- Bias mitigation: Avoiding disparities in responses across different populations.
- Privacy and security: Protecting sensitive patient information under HIPAA and GDPR.
- Over-reliance: Preventing patients from substituting chatbot interactions for professional medical advice.
Robust validation, robust guardrails, human-in-the-loop (HITL) and human-on-the-loop (HOTL) oversight are essential for maintaining patient safety.
What real-world examples highlight success?
Several healthcare providers have successfully implemented conversational agents:
- Cancer education bots that explain chemotherapy side effects and nutrition guidelines.
- Pregnancy chatbots guiding patients through trimester milestones and prenatal care.
- Mental health agents providing coping strategies, self-assessments, and crisis resources.
Studies show that conversational agents improve patient engagement, adherence to treatment, and satisfaction with education programs. Some programs even report reduced hospital readmission rates linked to better patient understanding.
What does the future of conversational agents in patient education look like?
Future advancements will bring:
- Multimodal conversational agents integrating voice, text, and video.
- Adaptive personalization leveraging patient feedback and outcomes to refine education delivery.
- Integration with wearables for real-time monitoring and contextual education.
- Regulatory-grade transparency ensuring chatbot recommendations remain auditable and safe.
John Snow Labs continues to innovate in this space, building explainable, domain-specific AI tools that power safe and effective conversational agents for healthcare organizations.
Why should healthcare programs adopt conversational agents?
Conversational agents provide a scalable, cost-effective, and engaging solution to improve patient education programs. They help patients understand conditions, follow treatments, and take ownership of their health journey. By combining accessibility, personalization, and transparency, these tools are transforming how healthcare organizations communicate with patients.
To explore how conversational agents can enhance your patient education programs, contact John Snow Labs today.
FAQs
What is a conversational agent in healthcare?
A conversational agent is an AI-powered chatbot or virtual assistant that interacts with patients to provide health education and support.
How do conversational agents improve patient education?
They deliver personalized, evidence-based information interactively, making health content easier to understand and recall.
Can conversational agents integrate with patient records?
Yes. With secure EHR integration, they can deliver tailored information based on patient-specific data.
Are conversational agents safe for medical use?
When built with healthcare-specific NLP and validated content as the tools developed by John Snow Labs, conversational agents can safely support education, though they must complement, not replace professional care.
What are the limitations of conversational agents?
They cannot diagnose conditions or replace clinician expertise but serve as supportive tools for patient engagement and education.
Supplementary Q&A
How do conversational agents support multilingual patient education?
By leveraging language models with multilingual capabilities, agents can provide culturally and linguistically appropriate education, reducing health disparities.
What role do conversational agents play in preventive healthcare?
They proactively share reminders about screenings, vaccinations, and healthy habits, empowering patients to adopt preventive practices.
How can healthcare organizations ensure chatbot accuracy?
By implementing regular clinical validation, continuous monitoring, and incorporating feedback from both clinicians and patients.
























 How do conversational agents support patient education programs?
How do conversational agents support patient education programs?



